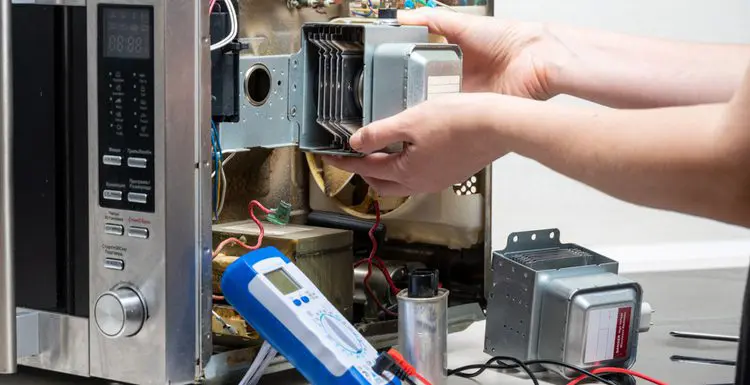
What makes the food cook so quickly?
There are several parts of a microwave, and they each have a specific role in heating your food.
They consist of internal components that help cook the food and external pieces that prevent radiation from escaping. In a nutshell, these include:
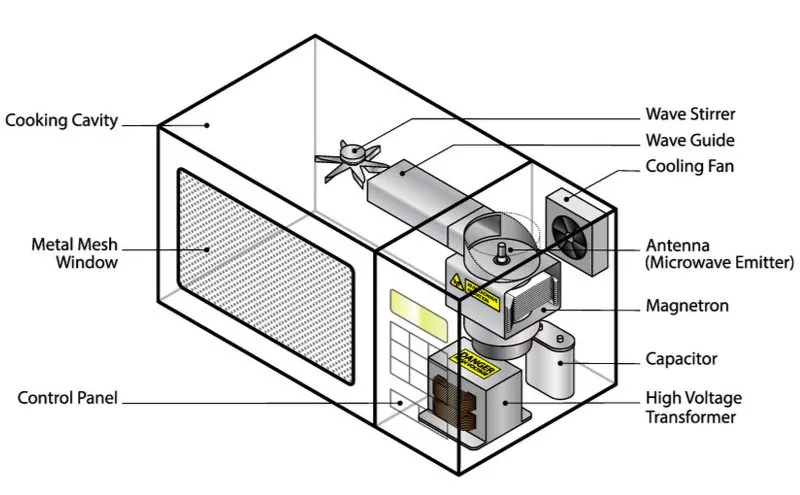
- Internal parts of a microwave: magnetrons, high-voltage transformer, waveguide, cooling fan, turntable, and cooking cavity.
- External components: case, power cord, door, and control panel.
This article will break down each component and its function and list precautions to take while using a microwave.
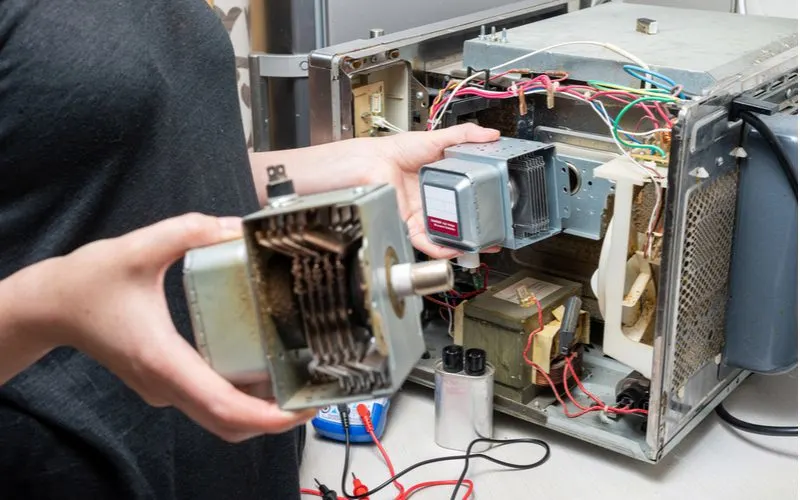
Parts of a Microwave Explained
Zern Liew/Shutterstock
The parts of a microwave are similar in all units but may vary to a degree. Each component performs a particular function to deliver thoroughly cooked meals safely and efficiently.
First, we’ll start with the internal components, which cook the food, and work our way to the external parts of a microwave.
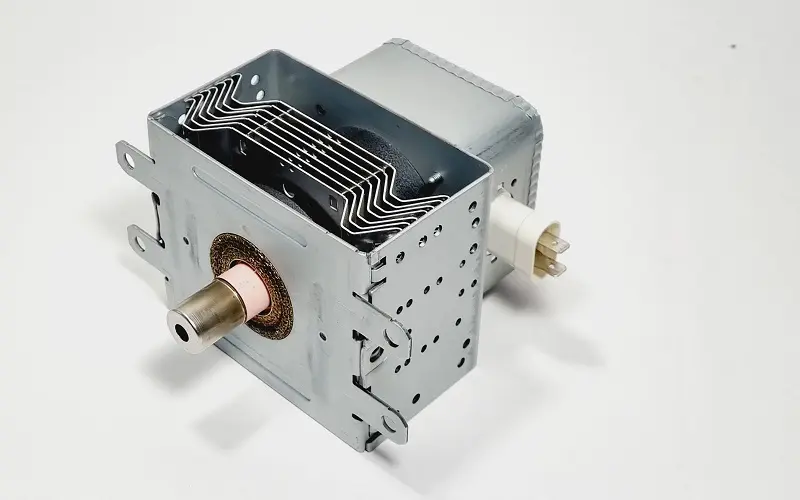
1. Magnetrons
Image/applianceparts365
The microwave’s magnetron consists of a vacuum-like tube and a strong magnet and sits on the same side as the control panel.
Like a human brain sends messages to the body, magnetrons produce microwaves that travel through the waveguide and bounce from the oven’s metal interior to the water molecules in the food.
The tiny waves cause the water molecules to vibrate. The friction of the vibrating molecules produces heat, thereby cooking the food.
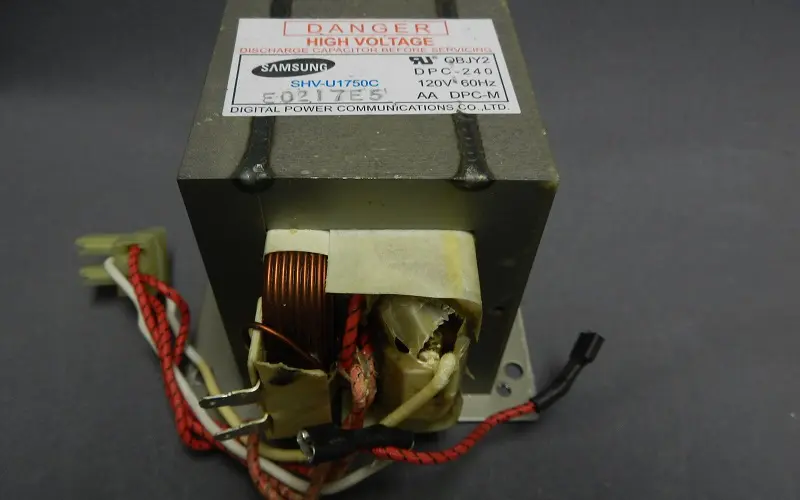
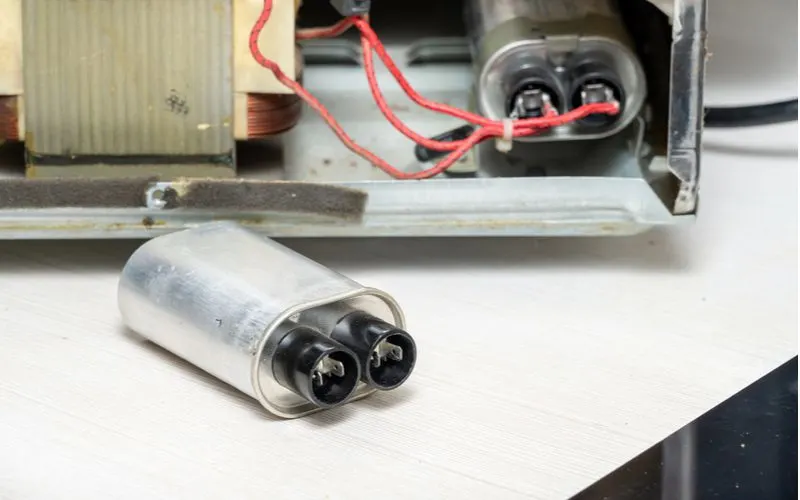
2. High-Voltage Transformer

Image/amazon.com
Most microwaves require at least 3000–4000 volts to heat food. Standard outlets use about 115 volts of power.
The high-voltage transformer converts that lower voltage into higher energy to cook food. As with any part, the size and power level will vary depending on the type of microwave you have.
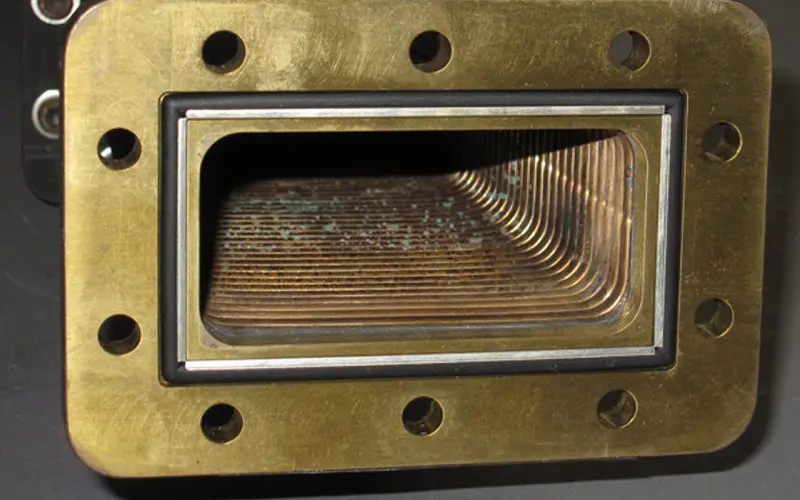
3. Waveguide

Image/theelectrostore.com
The waveguide is a hollow metal tube that extends from the magnetron to the cooling fan. It directs the flow of microwaves from the magnetron to the cooking chamber.
While these waves transfer, they reflect off the inner walls and into the food, cooking it. A waveguide includes a thin plastic or cardboard-like cover to protect the internal components from food and splatters during cooking.
It sits on the same side as the control panel. What happens if the protective layer comes off? Your microwave could suffer damage to the circuit boards, causing it to quit working.
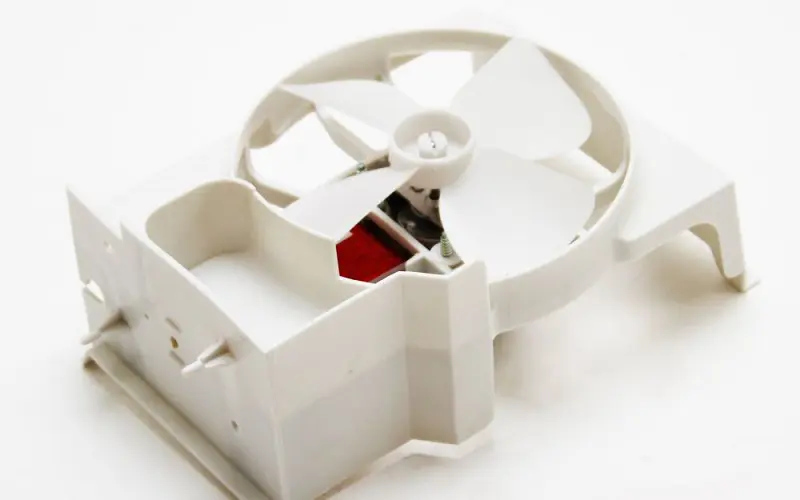
4. Cooling Fan
Image/walmart.com
The cooling fan, or stirrer in older versions, is a part of the microwave ceiling, with a covering to protect it against splatters. The fan prevents the unit from overheating. If too many heatwaves build up, not only will the food possibly burn.
But the appliance may become too hot (more than 150 degrees) and break down. When the microwave has been in use for a long time, it gets hot inside the chamber. The cooling fan knows when to turn on and off.
It automatically kicks on and begins to cool your kitchen appliance. If you notice it’s still running after you complete your heating cycle, don’t panic. It’s normal for it to stay on as long as necessary to cool the unit.
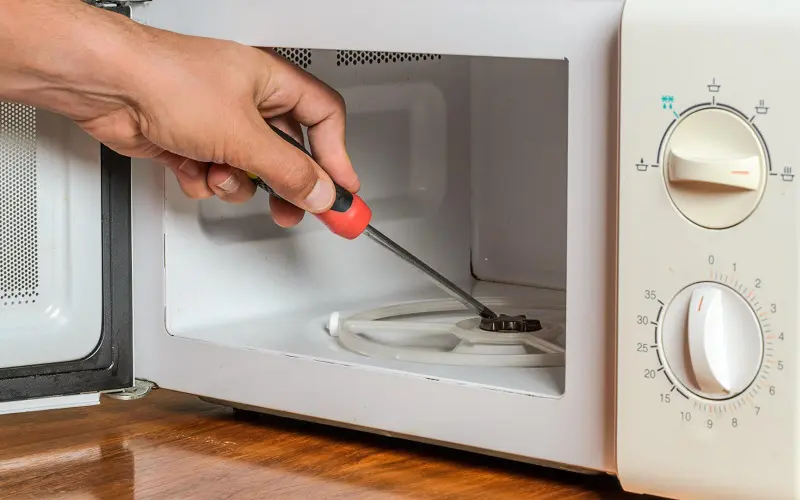
5. Cooking Cavity

Image/fleetappliance.com
The cooking cavity is the deep inner compartment that holds the food while it cooks. The inner walls consist of thick stainless steel to absorb the waves when they leave the food.
This cavity is where the turntable sits. The compartment keeps the inner air at room temperature so that your food doesn’t overcook.
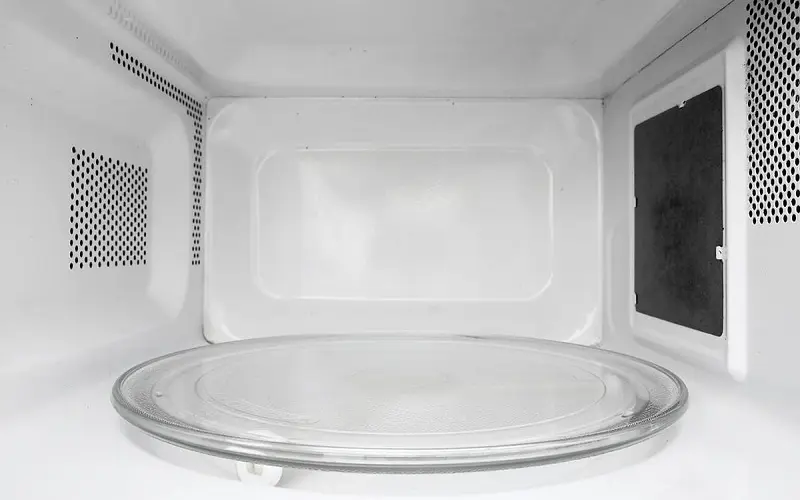
6. Turntable

Image/howdykitchen.com
You place your food on a round glass or plastic plate so that the food will rotate during cooking. The purpose of rotating your food is that heat will evenly distribute through it and cook it thoroughly.
All microwaves are different, but most turntables attach to an interlocking mechanism that rotates. Turntables are easy to remove and wash.
7. Exterior Case

Images/amazon.com
The outer case is the outer metal shell of the microwave that houses the inner components and cooking chamber.
Waves stay inside the cavity when the sealed door creates a seal to protect you from radiation during the cooking cycle.
8. Door

Image/housetrick.com
The door consists of a window to let you view your food. Some microwaves have a light that comes on during heating so that you can see clearly. A metal mesh lining between the glass layers prevents minute waves from leaking out.
This allows you to see in but keeps radiation away. The rubber seal around the door blocks radiation from leaking out. To ensure safety, the seal must be in good working condition. The presence of cracks could indicate wear and tear.
9. Control Panel
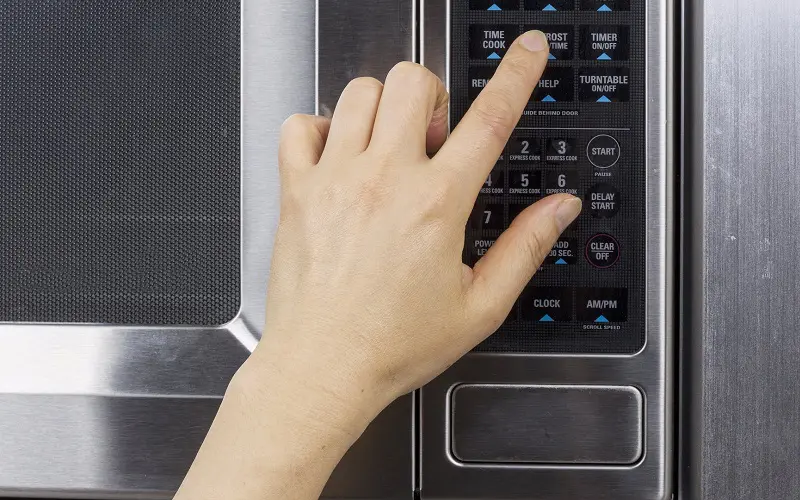

Shutterstock_121582243
Microwaves come with a control panel that allows you to choose your settings. Use a knob or buttons to determine the cooking time, cooking power, or mode, depending on what model you have.
Most appliances include a defrost setting, a timer, and a clock. Some units may include an option to pre-set cooking times.
All microwave control panels have a door-release button. You may have extra selections for potatoes, popcorn, or other types of food.
10. Power Cord
Kalabi Yau/Shutterstock
This component speaks for itself. It connects the microwave to electricity. You can detach the power cord from the back of the unit if you need to replace it.
Things to Consider

Kalabi Yau/Shutterstock
Although microwaves provide a low risk of radiation exposure, it is advisable to use them with caution.
- If you have a unit that is old and has broken parts, don’t try to use it. The possibility of electromagnetic radiation is higher when using a defective device. Inspect your oven for problem areas.
- One crucial safety step to take is to avoid standing directly in front of the appliance when it’s cooking. In case your oven is defective, you don’t want to risk exposure to radiation by being too close.
- Another smart move is to read the instruction manual before you begin the operation of the device. Each model of microwave may have safety features unique to its design. Proper use will reduce the risk of injury.
- Be sure to use microwave-safe containers because they don’t absorb as many radioactive waves as your food. The dishes won’t get as hot as your food.
Frequently Asked Questions

Image/Avalon_Studio
Are microwave ovens safe for heating food?
Yes, as long as you follow the manufacturer's instructions on how to use the appliance properly.
If you take care of the device, the parts of your microwave will work correctly. The radiation from a microwave only heats the food.
What is a safe power leakage for a microwave oven?
According to the FDA, five milliwatts of radiation per square centimeter is tolerable at about two inches from the oven’s surface. Dangerous levels are far from this figure.
What happens if I use metal in a microwave oven?
Nothing dangerous will happen to you, and your microwave won’t combust. The main downside is that the tiny cooking waves can’t flow through metal, so your food may not heat up.
If you place a sharp metal object in the microwave, it could spark. Smooth metal containers most likely won’t cause a reaction. Your best bet is to use glass, polyethylene, or other microwave-safe dishes to cook your meal.
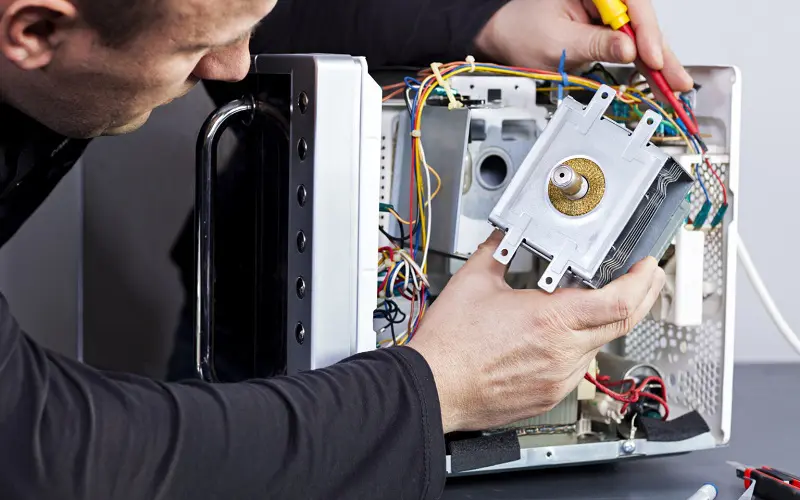
Are parts of a microwave replaceable?
It depends on the components. If you have a cheaper microwave, the parts may cost more than a new microwave. The door is easy to replace. There are no mechanical parts to order. You can probably find a new turntable or roller guide if they break.
You can access the spinning motor underneath the microwave and replace it. The control panel connects to a core computer so replacing the entire appliance will be the cheaper option. Don’t try to make any repairs yourself.
Can I get cancer from using a microwave?
The radiation from a microwave is non-ionizing or electromagnetic, which your cell phone uses the same kind of radiation, only stronger. It doesn’t threaten human cells as long as your unit is working correctly.
The exterior casing and door of the appliance prevent any radiation from escaping. For extra safety, experts recommend keeping at least a foot distance away from the microwave while it’s on.
Is it safe to use a microwave with a pacemaker?
Most modern pacemakers can avoid electrical interferences from appliances, like a microwave oven. It depends on the age of your pacemaker. If you have concerns, talk with your doctor.
Why does my microwave make noise after I open the door and remove my food?
The noise you hear is the cooling fan. Sometimes the oven gets too hot, and the fan must cool it down. It’s normal for the fan to stay on a few minutes after cooking is complete.
So, What Are the Parts of a Microwave?

Andrey_Popov/Shutterstock
What are the parts of a microwave? They consist of internal and external components that heat the food.
The internal parts of a microwave include the magnetron, high-voltage transformer, waveguide, cooling fan, turntable, and cooking cavity.
The external parts of a microwave are the case, power cord, door, and control panel.